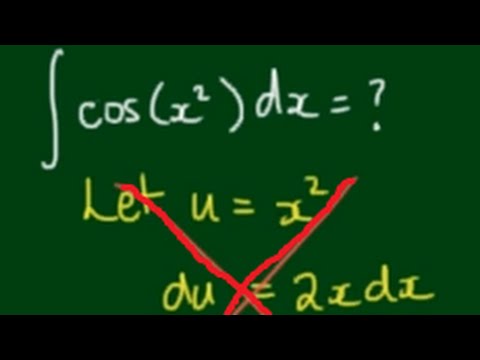![SOLVED:Evaluate the integral by choosing a convenient order of integration: ∬R x cos(x y) cos^2 πx d A ; R=[0, (1)/(2)] ×[0, π] SOLVED:Evaluate the integral by choosing a convenient order of integration: ∬R x cos(x y) cos^2 πx d A ; R=[0, (1)/(2)] ×[0, π]](https://cdn.numerade.com/previews/c5f6f0be-87de-4143-ae01-79191a5e3105_large.jpg)
SOLVED:Evaluate the integral by choosing a convenient order of integration: ∬R x cos(x y) cos^2 πx d A ; R=[0, (1)/(2)] ×[0, π]
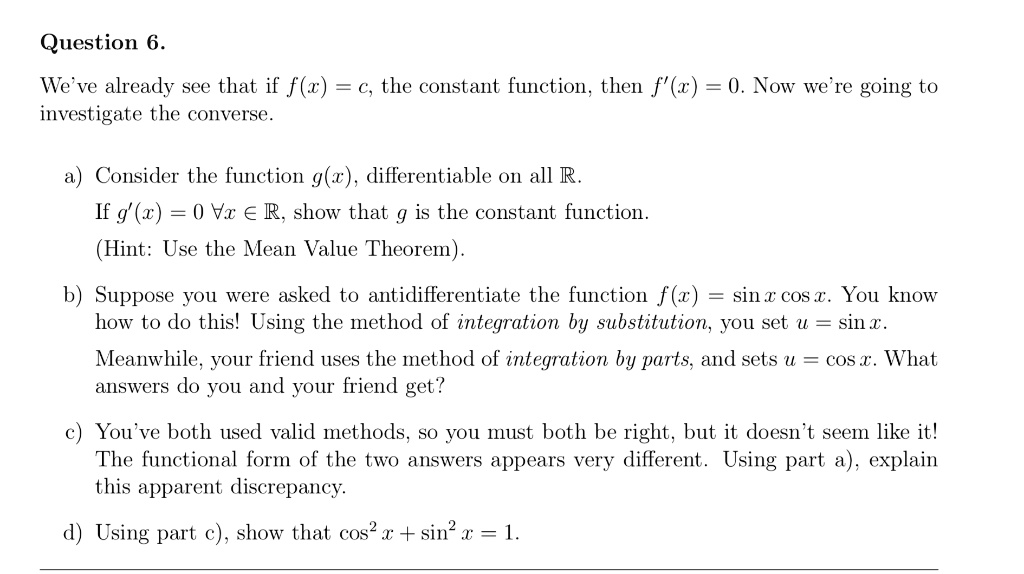
SOLVED: Question 6 We ve already see that if f() = C€, the constant function; then f' (x) 0. Now we re going to investigate the converse. Consider the function g(z) ,
What is the (indefinite) integral of the cosine function with an arbitrary frequency and phase shift? - Quora
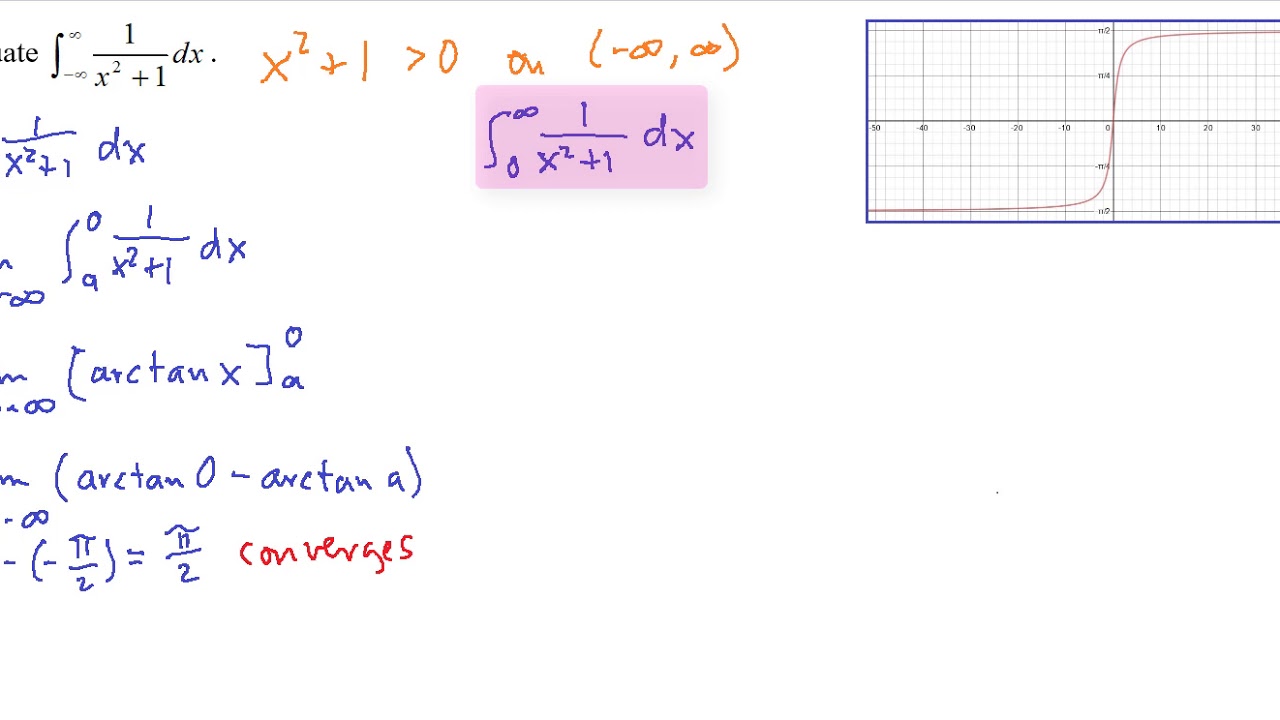













![ANSWERED] Use the Hinge Theorem and its converse to describe ... - Geometry ANSWERED] Use the Hinge Theorem and its converse to describe ... - Geometry](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20230519203247456634-5636345.jpg)